Can You Get to South Satellite From B Gates?
What is a satellite?

A satellite is an object in infinite that orbits or circles effectually a bigger object. There are two kinds of satellites: natural (such as the moon orbiting the Earth) or artificial (such as the International Space Station orbiting the Earth).
At that place are dozens upon dozens of natural satellites in the solar organisation, with nearly every planet having at least i moon. Saturn, for instance, has at least 53 natural satellites, and between 2004 and 2017, it besides had an bogus 1 — the Cassini spacecraft, which explored the ringed planet and its moons.
Artificial satellites, however, did not become a reality until the mid-20th century. The offset bogus satellite was Sputnik, a Russian beach-ball-size infinite probe that lifted off on Oct. four, 1957. That act shocked much of the western world, equally it was believed the Soviets did not have the adequacy to send satellites into infinite.
Brief history of artificial satellites
Post-obit that feat, on Nov. three, 1957 the Soviets launched an even more massive satellite — Sputnik two — which carried a dog, Laika. The United States' first satellite was Explorer 1 on January. 31, 1958. The satellite was merely 2 pct the mass of Sputnik 2, still, at thirty pounds (13 kg).
The Sputniks and Explorer 1 became the opening shots in a space race between the U.s. and the Soviet Matrimony that lasted until at to the lowest degree the late 1960s. The focus on satellites as political tools began to give manner to people every bit both countries sent humans into space in 1961. Afterwards in the decade, all the same, the aims of both countries began to split. While the United States went on to state people on the moon and create the space shuttle, the Soviet Union synthetic the world's first space station, Salyut i, which launched in 1971. (Other stations followed, such every bit the United States' Skylab and the Soviet Marriage's Mir.)
Other countries began to send their own satellites into infinite as the benefits rippled through order. Weather condition satellites improved forecasts, fifty-fifty for remote areas. Land-watching satellites such every bit the Landsat series (on its ninth generation at present) tracked changes in forests, h2o and other parts of Earth'southward surface over fourth dimension. Telecommunications satellites fabricated long-distance phone calls and eventually, live idiot box broadcasts from across the world a normal role of life. Later on generations helped with Internet connections.
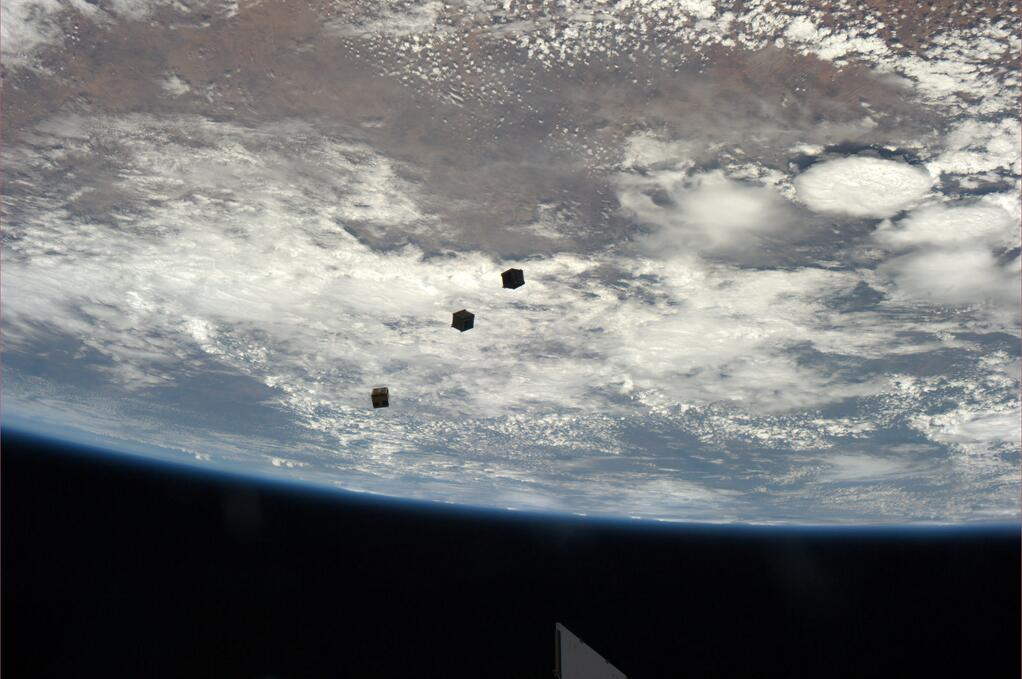
With the miniaturization of computers and other hardware, it's now possible to send up much smaller satellites that can practice scientific discipline, telecommunications or other functions in orbit. It's mutual now for companies and universities to create "CubeSats", or cube-shaped satellites that ofttimes populate low-Earth orbit.
These tin be lofted on a rocket forth with a bigger payload, or sent from a mobile launcher on the International Infinite Station (ISS). NASA is at present considering sending CubeSats to Mars or to the moon Europa (near Jupiter) for future missions, although the CubeSats aren't confirmed for inclusion.
The ISS is the biggest satellite in orbit, and took over a decade to construct. Piece by slice, 15 nations contributed financial and physical infrastructure to the orbiting complex, which was put together between 1998 and 2011. Plan officials expect the ISS to keep running until at least 2024.
Parts of a satellite
Every usable bogus satellite — whether it's a human or robotic one — has iv main parts to information technology: a power arrangement (which could be solar or nuclear, for example), a way to control its attitude, an antenna to transmit and receive information, and a payload to collect information (such as a camera or particle detector).
As will be seen below, however, not all artificial satellites are necessarily workable ones. Even a spiral or a bit of pigment is considered an "bogus" satellite, even though these are missing these parts.
What keeps a satellite from falling to Earth?
A satellite is best understood as a projectile, or an object that has simply ane forcefulness acting on it — gravity. Technically speaking, anything that crosses the Karman Line at an altitude of 100 kilometers (62 miles) is considered in space. However, a satellite needs to exist going fast — at to the lowest degree 8 km (5 miles) a 2d — to cease from falling back downwards to Earth immediately.
If a satellite is traveling fast enough, it will perpetually "autumn" toward Globe, but the Globe's curvature means that the satellite will fall around our planet instead of crashing dorsum on the surface. Satellites that travel closer to Earth are at take chances of falling because the elevate of atmospheric molecules volition irksome the satellites downward. Those that orbit farther away from Globe accept fewer molecules to contend with.
In that location are several accepted "zones" of orbits around the Earth. One is called low-World-orbit, which extends from about 160 to 2,000 km (about 100 to ane,250 miles). This is the zone where the ISS orbits and where the infinite shuttle used to practise its work. In fact, all human being missions except for the Apollo flights to the moon took place in this zone. Most satellites besides piece of work in this zone.
Geostationary or geosynchronous orbit is the best spot for communications satellites to utilise, however. This is a zone above Earth'due south equator at an altitude of 35,786 km (22,236 mi). At this altitude, the rate of "fall" around the Earth is almost the aforementioned as Earth's rotation, which allows the satellite to stay above the same spot on Earth almost constantly. The satellite thus keeps a perpetual connection with a fixed antenna on the basis, assuasive for reliable communications. When geostationary satellites reach the end of their life, protocol dictates they're moved out of the style for a new satellite to have their place. That's considering in that location is only and so much room, or so many "slots" in that orbit, to allow the satellites to operate without interference.
While some satellites are best used around the equator, others are meliorate suited to more polar orbits — those that circle the Earth from pole to pole and so that their coverage zones include the due north and south poles. Examples of polar-orbiting satellites include weather satellites and reconnaissance satellites.

What stops a satellite from crashing into another satellite?
There are an estimated half-meg artificial objects in Earth orbit today, ranging in size from paint flecks upward to full-fledged satellites — each traveling at speeds of thousands of miles an hour. Only a fraction of these satellites are useable, pregnant that there is a lot of "space junk" floating effectually out there. With everything that is lobbed into orbit, the take a chance of a collision increases.
Infinite agencies take to consider orbital trajectories carefully when launching something into space. Agencies such as the U.s. Infinite Surveillance Network keep an eye on orbital droppings from the footing, and warning NASA and other entities if an errant slice is in danger of hitting something vital. This means that from time to fourth dimension, the ISS needs to perform evasive maneuvers to go out of the mode.
Collisions still occur, however. I of the biggest culprits of space debris was the leftovers of a 2007 anti-satellite test performed by the Chinese, which generated debris that destroyed a Russian satellite in 2013. Too that year, the Iridium 33 and Creation 2251 satellites smashed into each other, generating a cloud of debris.
NASA, the European Space Agency and many other entities are considering measures to reduce the amount of orbital debris. Some suggest bringing down dead satellites in some fashion, perhaps using a internet or air bursts to disturb the debris from its orbit and bring it closer to Globe. Others are thinking about refueling expressionless satellites for reuse, a engineering that has been demonstrated robotically on the ISS.
Moons around other worlds
Most planets in our solar system have natural satellites, which nosotros besides call moons. For the inner planets: Mercury and Venus each have no moons. Earth has i relatively big moon, while Mars has two asteroid-sized pocket-sized moons called Phobos and Deimos. (Phobos is slowly spiralling into Mars and will probable break apart or fall into the surface in a few thousand years.)
Across the asteroid belt, are four gas giant planets that each have a pantheon of moons. As of late 2018, Jupiter has 79 confirmed moons, Saturn has 53, Uranus has 27 and Neptune has 14. New moons are occasionally discovered – mainly by missions (either past or nowadays, as nosotros can analyze old pictures) or by performing fresh observations by telescope.
Saturn is a special instance because information technology is surrounded by thousands of small objects that class a ring visible even in small-scale telescopes from World. Scientists watching the rings shut-up over 13 years, during the Cassini mission, saw conditions in which new moons might be built-in. Scientists were particularly interested in propellers, which are wakes in the rings created by fragments in the rings. Just after Cassini's mission ended in 2017, NASA said it's possible the propellers share elements of planet formation that takes place around young stars' gassy discs.
Fifty-fifty smaller objects take moons, nevertheless. Pluto is technically a dwarf planet. Nonetheless, the people behind the New Horizons mission, which flew by Pluto in 2015, debate its various geography makes information technology more than planet-like. One thing that isn't argued, all the same, is the number of moons around Pluto. Pluto has five known moons, most of which were discovered when New Horizons was in development or en route to the dwarf planet.
A lot of asteroids have moons, too. These small worlds sometimes fly close to the Earth, and the moons popular out in observations with radar. A few famous examples of asteroids with moons include iv Vesta (which was visited by NASA'due south Dawn mission), 243 Ida, 433 Eros, and 951 Gaspra. There are likewise examples of asteroids with rings, such as 10199 Chariklo and 2060 Chiron.
Many planets and worlds in our solar arrangement have human-made "moons" equally well, particularly around Mars — where several probes orbit the planet doing observations of its surface and surround. The planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn all had artificial satellites observing them at some bespeak in history. Other objects had artificial satellites every bit well, such as Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (visited by the European Space Agency's Rosetta mission) or Vesta and Ceres (both visited by NASA'due south Dawn mission.) Technically speaking, during the Apollo missions, humans flew in bogus "moons" (spacecraft) around our own moon betwixt 1968 and 1972. NASA may fifty-fifty build a "Deep Space Gateway" space station near the moon in the coming decades, equally a launching point for human Mars missions.
Fans of the movie "Avatar" (2009) will remember that the humans visited Pandora, the habitable moon of a gas giant named Polyphemus. We don't know yet if there are moons for exoplanets, but nosotros suspect — given that the solar system planets have so many moons — that exoplanets have moons as well. In 2014, scientists made an observation of an object that could exist interpreted every bit an exomoon circling an exoplanet, but the ascertainment can't be repeated as it took identify as the object moved in front of a star. Still, a second exomoon might have been found very recently.
Additional resource
- Read virtually some of the satellites that NASA has in orbit around Earth.
- Learn about the types of orbit that we put satellites in.
- Discover how satellites can prepare us for the increasing frequency of flood events around the earth.
Bibliography
Joukowsky Institute, Brownish University, "thirteen Things - space"
Amanda Barnett, NASA'due south Jet Propulsion Laboratory for NASA'southward Scientific discipline Mission Directorate, "Basics of Space Flight - Section 1: Environment, Chapter 5: Planetary Orbits"
Astromaterials Enquiry & Exploration Science, NASA, "The Orbital Droppings Issue"
Join our Infinite Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more than! And if yous have a news tip, correction or comment, allow us know at: community@space.com.
Source: https://www.space.com/24839-satellites.html
0 Response to "Can You Get to South Satellite From B Gates?"
Publicar un comentario